
China does not have a sampling frame for religious venues. The CRS sampling frame is made from different dataset. From the 2004 China Economic Census, we extract a religious organization dataset. Then we combine this dataset with the Sixth National Census, and establish a sampling frame for the China Religion Survey.
We use a probability proportional sampling (PPS) method to select our samples, and county is our primary sampling unit (PSU). In this wave of CRS, wehave selected around 5000 religious venues from 243 counties in 31 provinces.Our samples are nationally represenatative. We not only interview religious leaders but also governmental officials who are in charge of religious affirs.
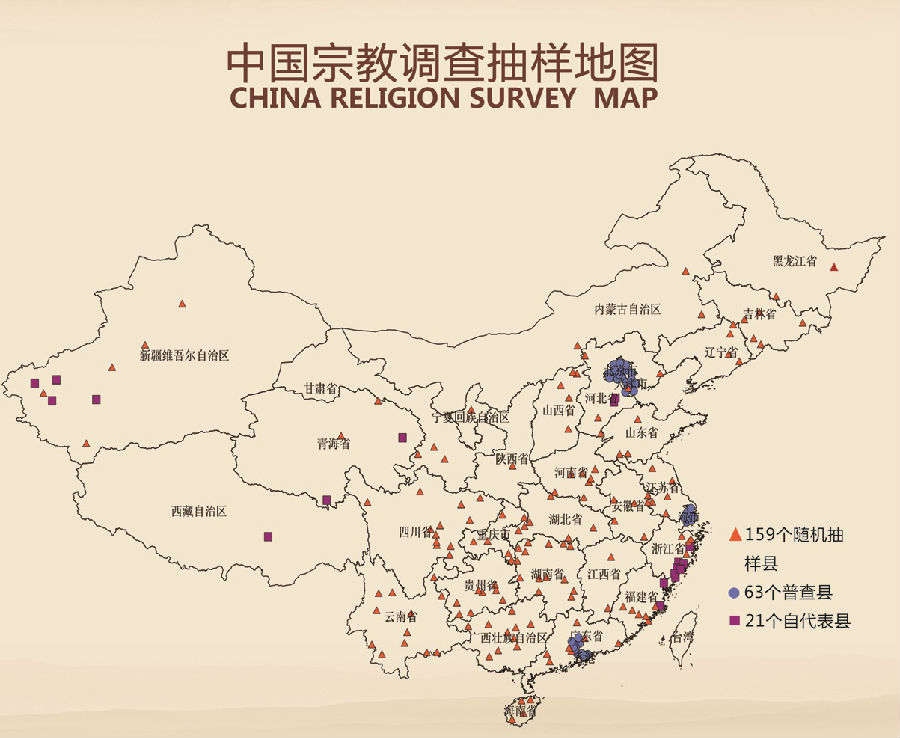
The sampling process can be divided into two stages. In the first stage,we select the PSU of CRS. The total number of PSUs is 243. Among them, 180 PSUs are randomly selected from the population. Then we also intentionally select the top 5 most religious counties of different religions. Due to someoverlapping, we get 21 PSUs. In order to understand the religious development in five most influential metropolitians, we also conduct a census on these areas, which adds 63 PSUs.
In the second stage, we select our second sampling units (SSU) within each PSU. The sampling method is as follow:
Table 1. The Sampling Method of CRS
| No. | Number of Venues within Each Religion | Sample Size for Each Religion |
| 1 | Less than 7 | All shall be included. |
| 2 | 8-10 | 7 |
| 3 | 11-20 | 10 |
| 4 | 21-30 | 15 |
| 5 | More than 30 | 20 |
The sample size of CRS is shown in the following table.
Table 2. Sample Size of China Religion Survey
| Religious Venue | Around 5000 |
| County | 243 |
| Province | 31 |